

The tracks of a compact disc act as a diffraction grating, producing a separation of the colors of white light. The hydrogen gas in a thin glass tube is excited by an electrical discharge and the spectrum can be viewed through the grating. The illustration shows the hydrogen spectrum. It acts as a "super prism", separating the different colors of light much more than the dispersion effect in a prism. The diffraction grating is an immensely useful tool for the separation of the spectral lines associated with atomic transitions. However, angular separation of the maxima is generally much greater because the slit spacing is so small for a diffraction grating. The condition for maximum intensity is the same as that for a double slit. The relative widths of the interference and diffraction patterns depends upon the slit separation and the width of the individual slits, so the pattern will vary based upon those values. The overall grating intensity is given by the product of the intensity expressions for interference and diffraction.
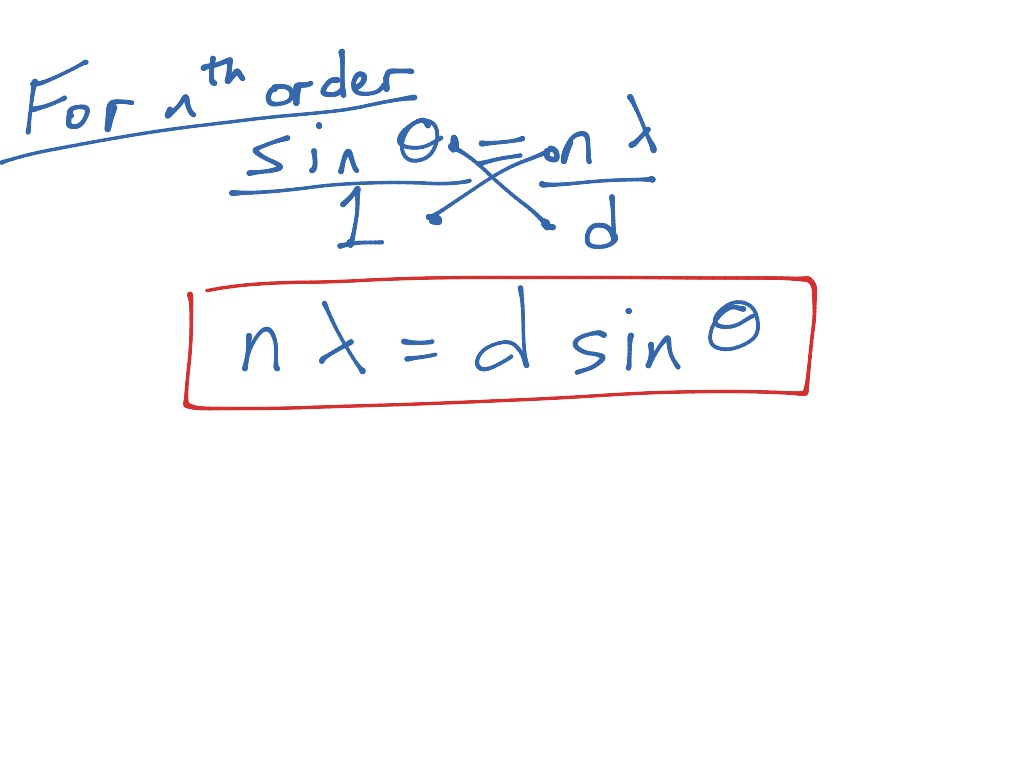
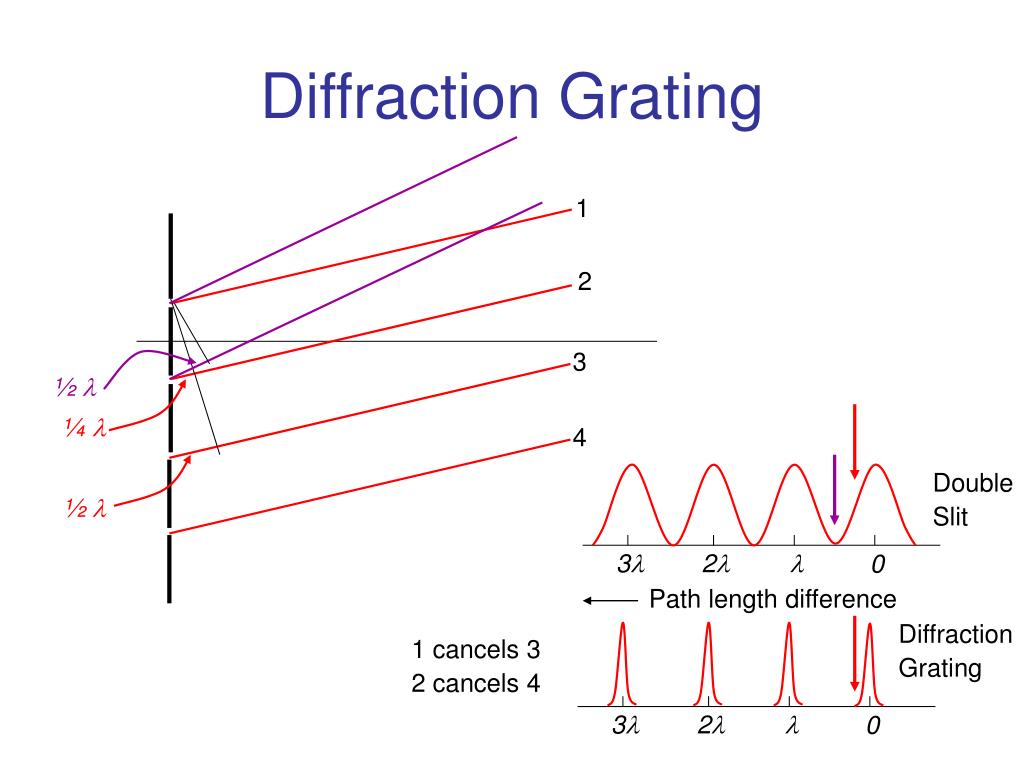
The intensities of these peaks are affected by the diffraction envelope which is determined by the width of the single slits making up the grating. There are multiple orders of the peaks associated with the interference of light through the multiple slits. This illustration is qualitative and intended mainly to show the clear separation of the wavelengths of light. Different wavelengths are diffracted at different angles, according to the grating relationship.Ī diffraction grating is the tool of choice for separating the colors in incident light. Orders 1 and 2 are shown to each side of the direct beam. When light of a single wavelength, like the 632.8nm red light from a helium-neon laser at left, strikes a diffraction grating it is diffracted to each side in multiple orders.

The peak intensities are also much higher for the grating than for the double slit. The condition for maximum intensity is the same as that for the double slit or multiple slits, but with a large number of slits the intensity maximum is very sharp and narrow, providing the high resolution for spectroscopic applications. A large number of parallel, closely spaced slits constitutes a diffraction grating. This "super prism" aspect of the diffraction grating leads to application for measuring atomic spectra in both laboratory instruments and telescopes. Therefore, the wavelength of light will ne 146.7 nano meter.When there is a need to separate light of different wavelengths with high resolution, then a diffraction grating is most often the tool of choice. In this formula, \(\theta\) is the angle of emergence at which a wavelength will be bright. This is known as the DIFFRACTION GRATING EQUATION. Constructive interference will occur if the difference in their two path lengths is an integral multiple of their wavelength \(\lambda\) i.e., The formula for diffraction grating:Ĭonsider two rays that emerge making the angle \(\theta\) with the straight through the line. Diffraction is an alternative way to observe spectra other than a prism. Also, if peaks fall on peaks and valleys fall on valleys consistently, then the light is made brighter at that point. If a peak falls on a valley consistently, then the waves cancel and no light exists at that point. Here Huygens’ Principle is applicable.Īccording to it every point on a wavefront acts as a new source, and each transparent slit becomes a new source so cylindrical wavefront spread out from each. Rays and wavefront form an orthogonal set so the wavefront will be perpendicular to the rays and parallel to the grating. 2 Solved Examples Diffraction Grating Formula Concept of the diffraction gratingĪ parallel bundle of the rays will fall on the grating.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
